TYPES OF SOLAR PV SYSTEMS in Pakistan
PV systems can be small and very simple, consisting of just a PV module and DC load. On the other hand, PV systems can also be built as large power plants with a peak power of several MW like Quaid-e-azam Solar Park Bahawalpur 100MW or 50MW Gharo Sindh: these are connected to the electricity grid. Many systems are placed on residential homes. When a whole house or building needs to be powered and is not connected to the electricity grid, the PV system must be operational day and night, It may also have to feed both Ac and Dc loads, have reserve power, and may even include a backup.
Depending on the system configurations, we can distinguish three main types of PV systems:
- Stand-alone/Off-Grid Systems
- On Grid / Grid Connected/ Grid Tie Systems
- Hybrid Systems
1.0 OFF-GRID SYSTEM
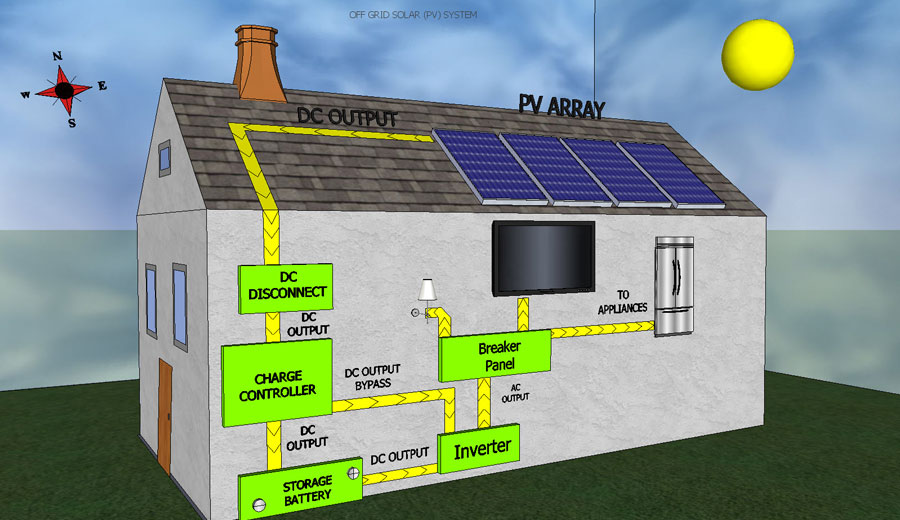
Off-grid solar electricity is for homes that do not have access to grid electricity – i.e the house cannot be or chooses not to be supplied electricity from a power company. These systems offer complete autonomy and independence from the national grid and power companies, meaning you never have an electricity bill. These panels generate electricity which is used to power your home and charge your batteries. The batteries allow you to store electricity for use at night or times of low production like cloudy days.
- This kind of a system will allow a customer to go off the grid
- However, these are the most expensive type as additional battery cost is incurred to provide a backup of up to 48 hours for a normal household or business functioning (including autonomy for a 1-2 rainy days)
- This is the most common installation type for areas that have no grid connection but are not very useful for urban areas.
- These systems are usually sized to not include air conditioning, as it is only a seasonal load. A larger system installed to meet peak summer demand will lead to wastage of power in the winters, making it un-economical
- Savings from the system lead to a payback period of up to 10 years. After that, you get free power for 10 more years
.
2.0 Grid-connected / On Grid Systems
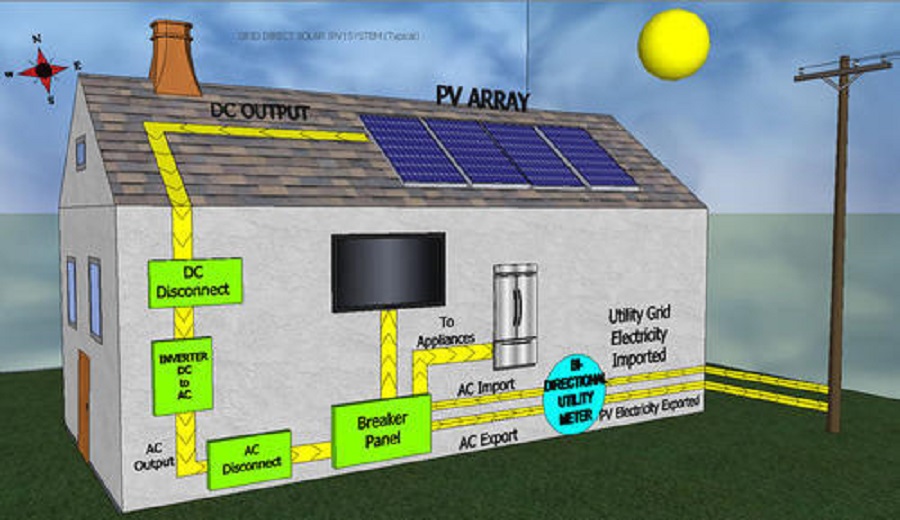
Grid-connected PV systems have become increasingly popular for applications in the built environment. They are connected to the grid via inverters, which convert the DC power into AC electricity. The inverter is connected to the distribution board, from where the PV generated power is transferred into the electricity grid or to AC appliances. In principle, these systems do not require batteries, since they are connected to the grid, which acts as a buffer into which an oversupply of PV electricity is transported. The grid also supplies the consumer with electricity in times of insufficient PV power generations.
- It is important to note that this type of system will not run if the grid is down and the diesel generator is also not running
- For this type of system, solar power is always given preference over both grid and diesel. An intelligent solar inverter ensures that solar is first fully utilized and then remaining power requirement is drawn from the grid or diesel generator
- Most systems being installed in Haryana for meeting obligations are also of this type.
- This is the most economically viable system as there is no requirement to install a battery bank. we recommend this system for customers who already have 100% power backup. When you install this system, you will still need to run the diesel generator when the power goes off but your fuel consumption will be lower.
3. Hybrid Systems
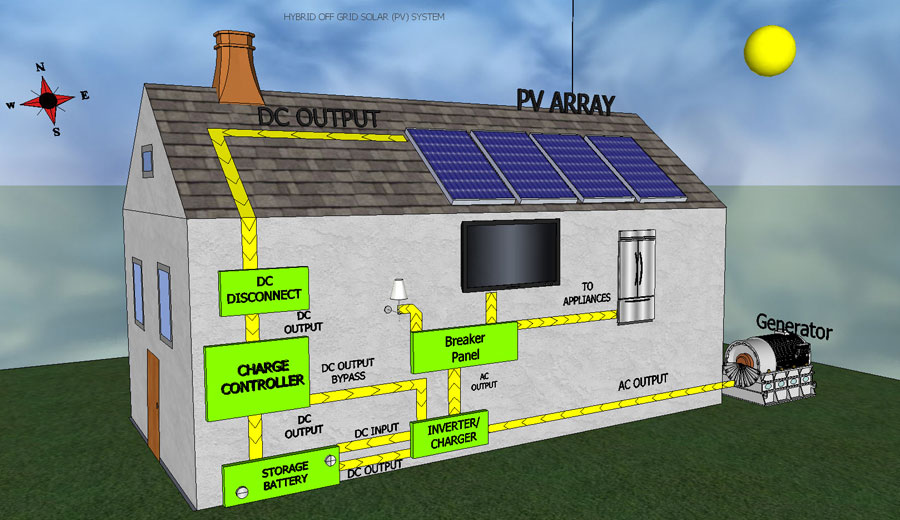
These systems combine PV module with a complementary method of electricity generation such as a diesel, gas or wind generator. In order to optimise system the different methods of electricity generations, hybrid system typically require more sophisticated controls than stand-alone or grid-connected PV system. For example, in the case of a PV/diesel system, the diesel engine must be started when the battery reaches a given discharge level, and stopped when the battery reaches an adequate charging state. The backup generator can be used to recharge batteries only or to supply the load as well.
- This type of system combines the benefits of both a grid tied system and an off-grid system. It is the most useful type of system for houses, bunglows, nursing homes and other smaller establishments. It acts like a home inverter.
- It allows for the system to provide 6-7 hours of backup for part of the load during power cuts (load-shedding) while still delivering the benefits of a grid-tied system.
- These systems are usually sized to not include air conditioning and other seasonal induction loads. A larger system installed to meet peak summer demand will lead to wastage of power in the winters, making it un-economical
- Perhaps one air-conditioner can be used on this system when the power goes out. It will just reduce the back-up hours to 4-5 hours. For running more A/Cs in a power cut, it is recommended that the customer use a diesel generator